Applications of Thermodynamics: Enthalpy
Applications of Thermodynamics: Enthalpy: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Enthalpy,Molar Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure (Cp),Relationship Between Cp and Cv for an Ideal Gas, etc.
Important Questions on Applications of Thermodynamics: Enthalpy
For the reaction :
at constant temperature is
When a electric heater is immersed in a gas for in a constant volume container with adiabatic walls, the temperature of the gas rises by . The heat capacity of the given gas is (Nearest integer)
Change in internal energy of an ideal gas is given by. Explain?
Heat of reaction for, at constant pressure is at . Calculate the heat of reaction at constant volume at .
Among the following standard enthalpy of formation is non-zero for
mol of is combusted in a fixed volume bomb calorimeter with excess of at and atm into . During the reaction, temperature increases from to . If heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter and enthalpy of formation of are and at , respectively, the calculated standard molar enthalpy of formation of at is . The value of is ____. [Given: Gas constant ]
What is enthalpy?
A heater was placed in of methanol and turned on for exactly for . The temperature increased by . Assuming that all the heat is absorbed by methanol, the molar heat capacity of methanol is
The difference between the value of of and of will be :
Which statement is correct?
The density of a substance is and that of another substance is . The heat capacity of of first substance is equal to that of of second substance. The ratio of their specific heats is
What is enthalphy?
Heat required to raise the temperature of of steam () by in a rigid and closed vessel is
Which of the following has lowest specific heat value
From the following data at constant volume for combustion of benzene, calculate the heat of this reaction at constant pressure condition.
, at .
of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes adiabatic expansion from against a constant external pressure of .
One mole ideal monoatomic gas is heated according to path and . If temperature of state and state are equal.
Calculate .
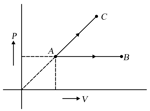
Round off your to the nearest integer.
A monoatomic ideal gas kept in a vessel fitted with a piston is expanded irreversibly from its initial state () to the final state (). The enthalpy and entropy changes in the process are, respectively
Value of for molecule is (Consider vibrational degree of freedom to be active)
A piece of metal weighing is heated to and dropped into of cold water in an insulated container at . If the final temperature of the water in the container is , the specific heat of the metal in . is
